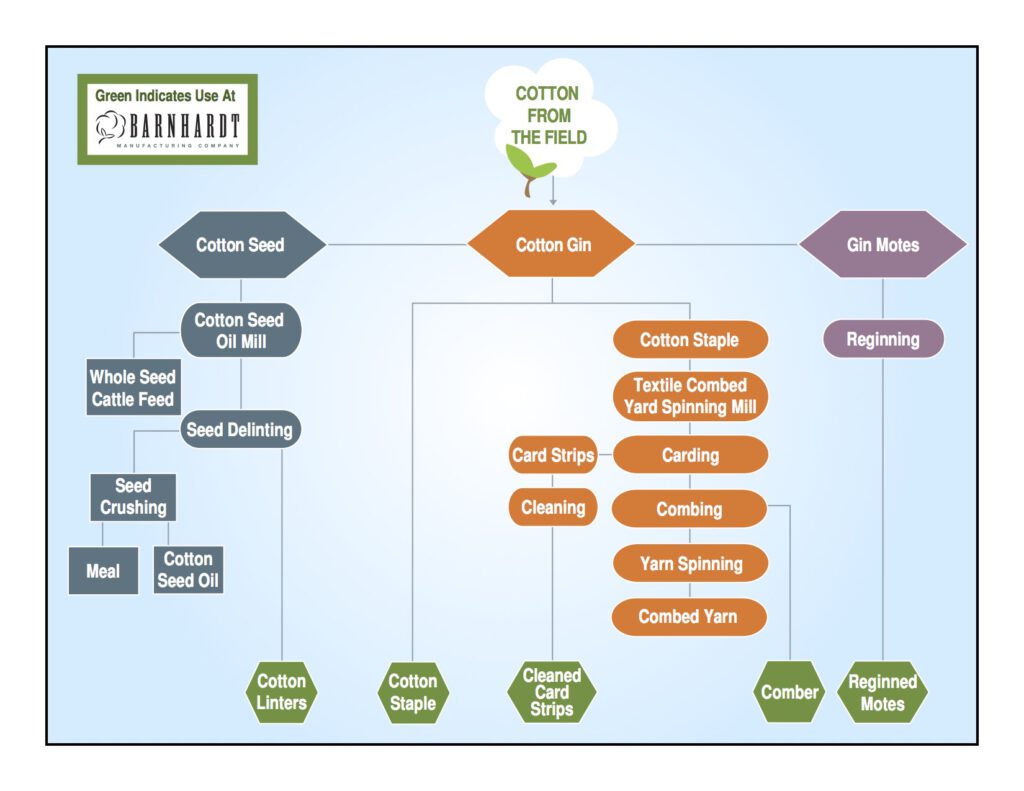
From the field to its arrival at Barnhardt Manufacturing Company, cotton goes through many steps before it arrives at our door. We illustrated the process cotton goes through – from the time it is picked to the time it is purified – in the cotton flow chart diagram below.
The blue boxes represent the cotton seed oil mill steps, the orange boxes represent the textile combed yarn spinning mill, and the purple boxes represent the gin mote reginning process. The green hexagons characterize the cotton used in Barnhardt’s purification process.
Cotton Fiber Glossary
Cotton Gin – Short for engine, all fiber from the field flows through the cotton gin. Today’s modern cotton gins dry and clean the cotton – removing field trash and plant parts like sticks and stems – before performing the primary job of removing fiber from the seed.
Cotton Staple, Virgin Cotton, Raw Cotton, #1 Raw Cotton – Cotton fibers that are removed from the cotton seed by the gin. This is the main product from the gin and is sold on the open market. The by-products of the gin are cotton seed and gin motes.
Cotton Seeds – Seeds removed from the fiber by the gin that are then collected and sold. Short fibers (called cotton linters) that the gin could not remove remain attached to the cotton seeds.
Cotton Seed Oil Mill – Mills that purchase and process cotton seeds.
Cotton Linters – Short fibers removed from cotton seeds by the cotton seed oil mill.
Gin Motes – Small, broken, or immature seeds with attached fibers. The gin removes the motes at a different stage from the mature, whole seeds.
Reginned Mote Fiber – Fiber removed by re-ginning machines from the gin motes.
Card – A machine used to separate, align, and remove of short fibers from cotton.
Carding – A process in yarn manufacturing where fibers are opened, cleaned, aligned, and formed into a continuous web.
Cleaned Card Strips – The waste fiber removed by the revolving flats of a card during the carding process.
Combing – Removing short fibers using combs from the continuous card web as part of the process to produce combed yarns.
Comber, Comber Noils, Noils – Short fibers removed in the combing process.
Additional Cotton Fiber Terms
Cellulose – The polymer that makes up cotton fibers.
Cotton Classing – The USDA tests every bale of staple cotton produced by US cotton gins. A High Volume Instrument measures fiber properties including fiber strength, length uniformity, micronaire, trash, and color. All of these values are attached to each bale, and fiber is purchased based on these properties.
Cotton Purification – Removal of oils, waxes, and color bodies from cotton fibers. At Barnhardt, this is accomplished using a chlorine-free process.
Micronaire – A measurement of airflow resistance through a standard weight of cotton compressed to a specific volume. The higher the value, the larger the diameter of the fibers. Micronaire range is normally 2- 5, although there are some fiber types that produce fibers with micronaire as high 8.
Nep – A small tangled bundle of fibers.
Scroop – A crunchy sound and feel when purified cotton is squeezed in one’s hand. Certain fiber finishes impart this quality.
USP Purified Cotton – Purified cotton fibers that meet the purity standards specified by United States Pharmacopeia.